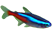
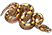Dwarf Leopard Boa stars and stripes (Boa Constrictor)
This animal is currently unavailable. Please get in touch to register your interest.
The Common Boa, scientifically known as Boa constrictor, is a large and robust snake species that can be found in various habitats throughout Central and South America.
One of the most remarkable features of the Common Boa is its size. It is considered one of the larger snake species, with adult individuals commonly reaching lengths of 6 to 10 feet, although some exceptional specimens can grow even longer.
In terms of temperament, Common Boas are generally docile and tolerant of handling, making them suitable for experienced snake enthusiasts as well as those new to reptile keeping. While individuals may vary in temperament, they often exhibit a calm demeanor when provided with proper care and a stress-free environment.
In the wild, Common Boas are highly adaptable, inhabiting a range of environments including forests, grasslands, and even semi-arid regions. They are primarily terrestrial but are also capable climbers, utilizing their strong muscles and prehensile tails to navigate their surroundings. Providing a spacious and secure enclosure that allows for both terrestrial and elevated areas is crucial for their well-being in captivity.
As carnivorous snakes, Common Boas feed on a diet of appropriately-sized prey, such as rodents, birds, or small mammals. They are constrictors, using their muscular bodies to wrap around their prey and suffocate it before consuming it whole. Providing a varied diet and ensuring proper husbandry conditions, including temperature and humidity, are essential for their overall health and vitality.
This animal was last updated in the past month. Please make sure to contact us before travelling long distances regarding this animal.
Any prices listed are subject to change, all final prices are decided in the shop.